LOCK FORMER
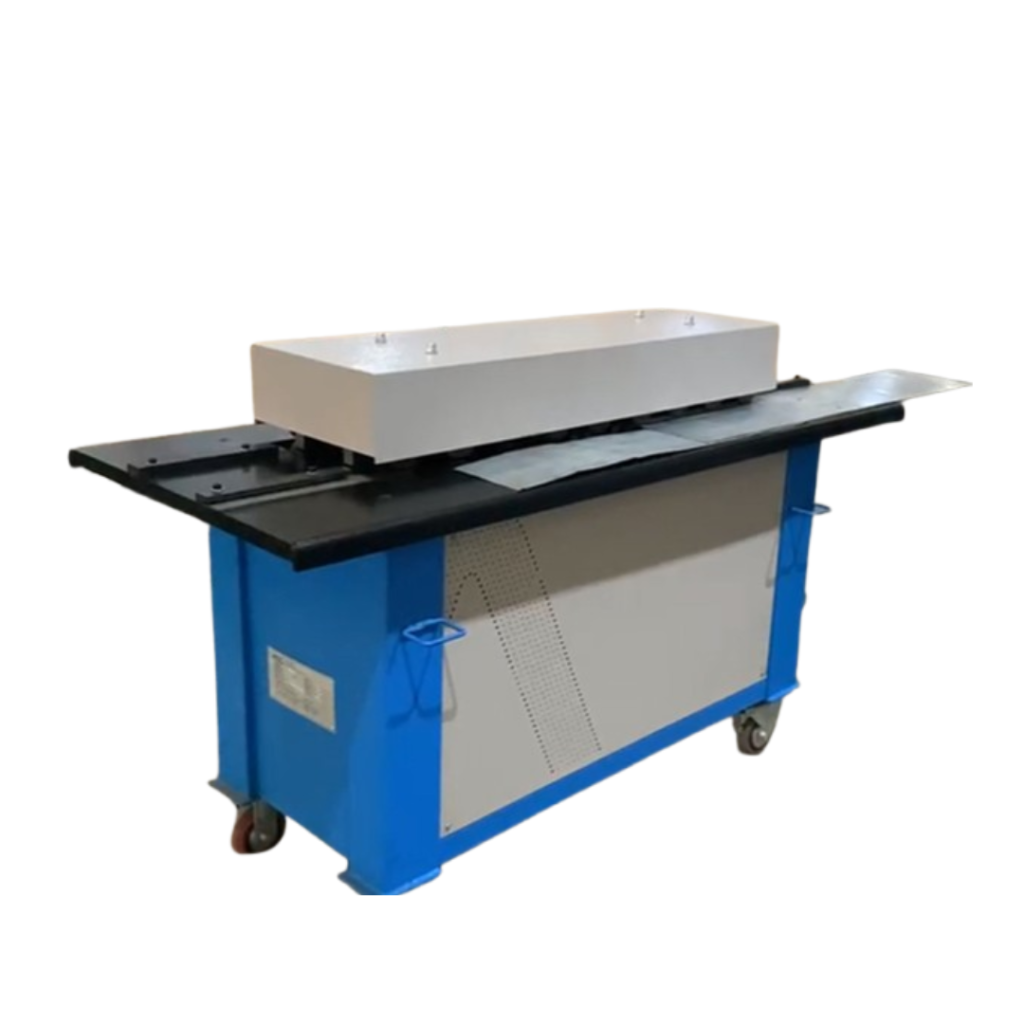

Introduction on Lock Former:
A Lock Former Machine is a specialized sheet metal forming machine designed to create strong, consistent folded seams, edges, and lock joints in sheet metal parts without welding. In sheet metal fabrication, creating durable connections — especially for ducts, enclosures, trays, and cabinets — requires reliable joining methods. The lock forming process folds and interlocks metal edges to produce joints that are both structurally sound and visually neat.
Lock Former Machines are widely used in metal working industries where seam integrity, airtightness, and mechanical strength are critical. Unlike welding or riveting — which may require skilled labor, additional consumables, or post‑finishing — a lock former produces consistent results with minimal finishing, low material waste, and higher repeatability.
Historically, sheet metal assemblies relied on manual hammer and anvil techniques to fold edges or simple mallets to force seams together. These methods were labor intensive, inconsistent, and time‑consuming. As industrial fabrication advanced, the need for more rapid, accurate, and reliable forming solutions led to the development of machines that could mechanically fold metal edges with precision. Lock Former Machines filled this niche by automating the edge forming process and ensuring uniform seams across batches.
Today’s lock formers range from compact benchtop units for light gauge work to robust floor‑standing machines capable of handling thick steel or aluminum sheets. Many models allow adjustable fold widths, depths, and angles — supporting a wide range of sheet sizes and materials.
As fabrication demands grow — driven by construction, HVAC systems, electrical enclosures, and industrial assemblies — lock former machines play an essential role in modern sheet metal operations. They reduce production time, improve joint quality, and help shops maintain high standards of repeatability, precision, and reliability at scale.
In this comprehensive guide, we explore everything you need to know about lock former machines — why they are indispensable in fabrication workflows, key features to consider, application scenarios, benefits they deliver, and limitations you should be aware of before investing.
Why to Use a Lock Former Machine ?
Consistent, High‑Quality Joints
One of the core reasons to use a lock former machine is the consistency of the joints it produces. Mechanical folding ensures every seam meets the same specifications, unlike manual techniques that vary with operator skill. Uniform seams are essential for structural integrity, especially in products that must withstand load, vibration, or internal pressure.
Eliminates the Need for Welds or Fasteners
Welding, rivets, or screws often introduce weak points, require skilled welders, add cost in consumables, and necessitate post‑finish work (grinding, polishing). Lock forming creates permanent mechanical joins without consumables, saving time and material cost
Enhanced Structural Integrity
A lock formed seam provides enhanced mechanical interlock that distributes stress more evenly than spot welds or rivets. This results in stronger assemblies and longer product life, particularly for panels, boxes, or duct sections where rigidity matters.
Reduced Labor Dependence
Manual lock forming demands experienced operators, and results can vary. A lock former machine standardizes the forming process, which means less reliance on manual skill, fewer errors, and easier training for new staff.
Improved Aesthetics and Precision
The edges and seams produced by lock forming machines are neat, precise, and repeatable. This is vital for products where surface appearance and dimension accuracy are critical — such as architectural panels or finished metal enclosures.
Integration With Fabrication Workflow
Lock former machines integrate well with other metalworking tools — such as shearing machines, press brakes, folder machines, or CNC systems — facilitating a smooth and efficient workflow in production lines.
Features:
Heavy‑Duty Frame and Precision Construction
A solid steel frame minimizes vibrations and ensures stability during forming. Rigid construction enables accurate folds and extends machine life.
Adjustable Forming Rollers & Dies
Lock former machines typically use rollers or forming dies that can be adjusted for:
– Fold width
– Fold depth
– Material thickness
– Radius of the fold
Multi‑Position Forming Capability
Higher‑end models allow:
– Vertical lock forming
– Horizontal lock forming
– Corner or compound fold forming
This flexibility expands the range of producible parts.
User‑Friendly Control Panels
Advanced units include digital or analog control interfaces for:
– Setting fold parameters
– Adjusting feed speed or forming pressure
– Storing preset configurations
– Monitoring forming cycles
Workpiece Support Tables & Guides
Large or thicker sheets need support during forming. Support tables, roller guides, and stable platforms help manage material and ensure accurate feeding.
Safety Features
Essential safety features include:
– Emergency stop buttons
– Guards around moving parts
– Two‑hand control options
– Safety interlocks
Applications:
HVAC Ductwork and Ventilation Systems
In HVAC fabrication, duct sections must be joined with secure seams to ensure:
– Airtightness
– Structural rigidity
– Reduced leakage
Electrical and Control Panel Enclosures
Manufacturers of control cabinets and enclosures use lock forming to create robust, seamless joints that support:
– Panel mounting
– Wiring access
– Grounding continuity
Automotive Body and Chassis Components
Lock forming processes are used to:
– Form heat shields
– Create box sections
– Produce panel edges
Metal Furniture and Store Fixtures
Assembly‑ready parts like shelves, drawers, and cabinets benefit from lock formed edges because:
– They eliminate sharp edges
– Improve strength
– Enhance appearance
Industrial Enclosures and Machinery Covers
Equipment housings and protective covers often employ lock joints for durability and ease of assembly.
Structural Sheet Metal Assemblies
Applications include:
– Brackets
– Supports
– Guard panels
Air Handling Units & Filtration Systems
Air handlers, plenums, and filter housings require tight, reliable folds to maintain airflow efficiency.
Heavy Equipment & Construction Fabrication
Lock formed seams are used in:
– Roof panels
– Trailer components
– Equipment trays
Custom Metal Work and Contract Fabrication
Lock former machines allow fabricators to produce custom parts quickly — a major advantage in bespoke orders or prototype development.
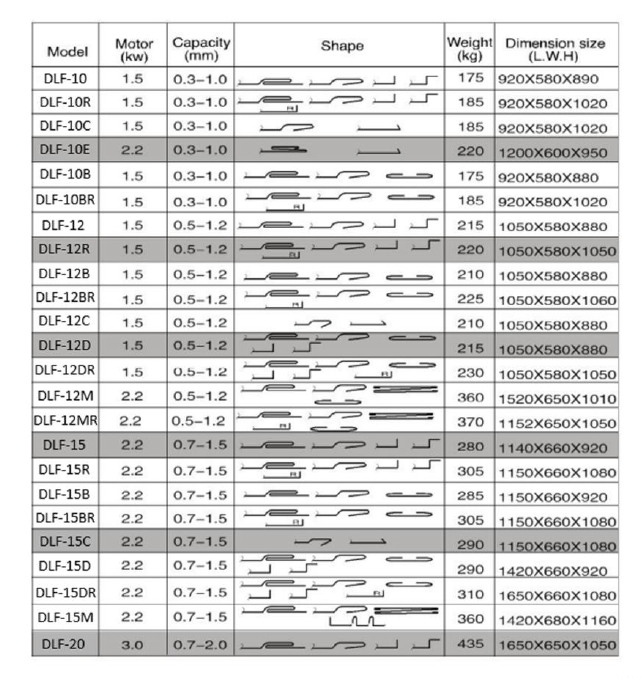
Technical Parameters: