Introduction to Pipe Threading Machine
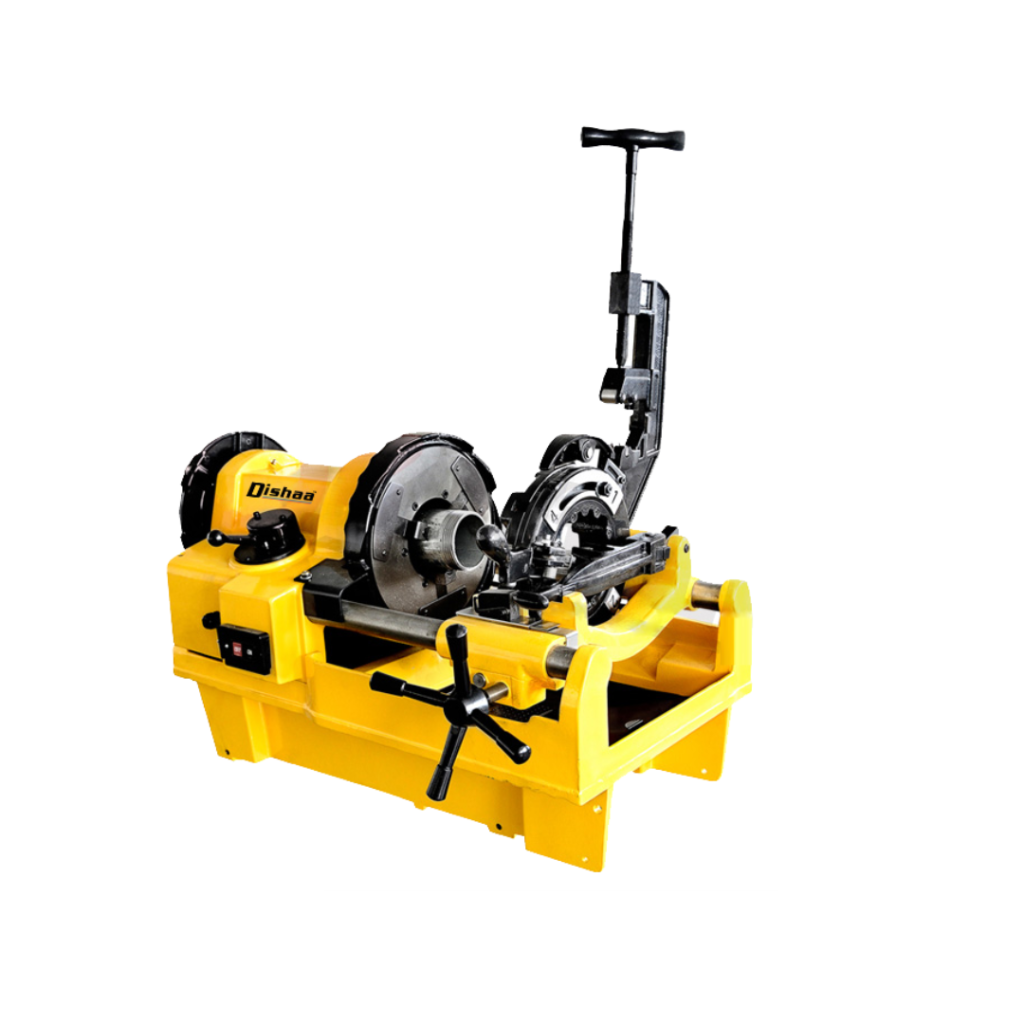
A Pipe Threading Machine is an essential tool used in various industries to cut threads on the ends of pipes, enabling them to be securely connected with fittings, valves, or other pipes. It plays a crucial role in creating leak-proof connections in plumbing, gas, fire protection, HVAC, and oil & gas pipelines. This machine offers precision, speed, and efficiency, especially in high-volume or industrial applications where manual threading would be time-consuming and inconsistent.
In traditional methods, threading was often done by hand, which required considerable skill and effort. However, with advancements in technology, automatic and semi-automatic pipe threading machines have replaced manual processes. These machines come equipped with electric motors, die heads, self-oiling systems, and adjustable speed settings, allowing operators to produce clean, uniform threads with minimal physical strain.
Most modern machines are designed to be portable or bench-mounted, making them versatile for on-site and workshop use. Some models also include built-in cutters, reamers, and oiling systems to improve accuracy and reduce wear on the dies.
One of the major advantages of using a pipe threading machine is the consistency and quality of threads it produces. Unlike manual threading, which can vary depending on the operator’s skill, a machine ensures that each thread is precise, which is critical for maintaining safety and performance in pressurized systems. Additionally, the speed and automation provided by the machine significantly increase productivity in large-scale operations.
Pipe threading machines come in different types based on their power source and design:
Manual Pipe Threading Machines: Ideal for small jobs or portable use, these are hand-operated and suited for low-volume work.
Electric Pipe Threading Machines: These are powered by electric motors and are widely used in commercial and industrial applications. They offer better efficiency and can handle larger pipe diameters.
Hydraulic Pipe Threading Machines: Used in heavy-duty industrial environments where threading large pipes with thick walls is necessary. They are robust, high-performing, and durable.
Applications:
1. Plumbing & Sanitary Works
– Used to create threaded joints for water supply, drainage, and piping systems.
– Essential for residential, commercial, and industrial plumbing installations.
2. Oil & Gas Industry
– Threads heavy-duty pipes for drilling rigs, pipelines, and refineries.
– Ensures leak-proof connections in high-pressure environments.
3. Construction & Infrastructure
– Used in building construction for HVAC systems, fire sprinkler installations, and structural piping.
– Ensures precision in large-scale mechanical installations.
4. Manufacturing Units
– Supports in-house fabrication of threaded components and pipe assemblies.
– Increases productivity in fabrication workshops.
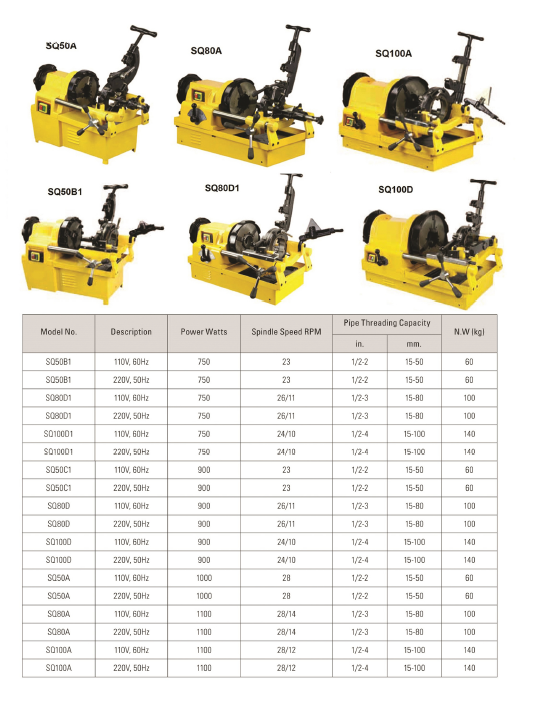
Parameters: